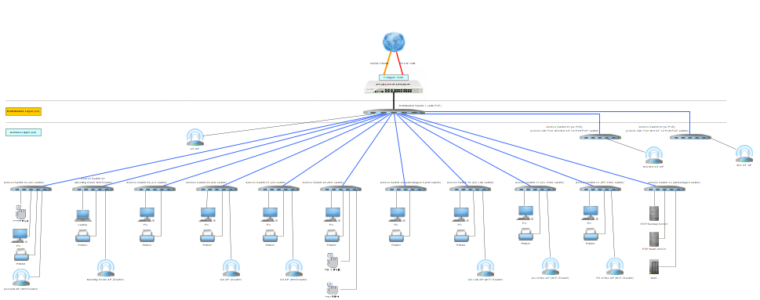
Best Practices for Network Wiring: Implementing Multi-Layer Concepts for Optimal Performance
Introduction:
Effective network wiring is essential for ensuring reliable connectivity, optimal performance, and scalability in small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs). By adhering to best practices and leveraging multi-layer concepts suggested by CISCO, organizations can design and implement structured cabling solutions that support their current needs while accommodating future growth. In this article, we’ll explore the fundamentals of network wiring, the concepts of layers 1, 2, and 3, as well as multi-layer switches. We’ll also provide detailed guidance on implementing best practices for network wiring, accompanied by network diagram references for better understanding.
Understanding Layers 1, 2, and 3:
1. Layer 1 (Physical Layer):
- The Physical Layer encompasses the physical components of a network, including cables, connectors, switches, and network interface cards (NICs).
- Its primary function is to establish and maintain the physical connection between devices, ensuring reliable transmission of data signals.
- Examples of Layer 1 devices include Ethernet cables, fiber-optic cables, patch panels, and network switches.
2. Layer 2 (Data Link Layer):
- The Data Link Layer is responsible for the reliable transfer of data between adjacent network nodes over a physical link.
- It provides error detection, flow control, and framing of data packets, ensuring efficient and error-free communication between devices.
- Examples of Layer 2 devices include switches, bridges, and network interface cards (NICs).
3. Layer 3 (Network Layer):
- The Network Layer facilitates end-to-end communication between devices across different networks by routing data packets based on IP addresses.
- It enables logical addressing, packet forwarding, and routing decisions, allowing devices to communicate across interconnected networks.
- Examples of Layer 3 devices include routers, Layer 3 switches, and IP-enabled devices such as computers and servers.
Understanding Multi-Layer Switches:
- Multi-layer switches combine the functions of Layer 2 switching and Layer 3 routing within a single device, offering enhanced flexibility and performance for network communication.
- They can make forwarding decisions based on both MAC addresses (Layer 2) and IP addresses (Layer 3), allowing for efficient packet switching and routing within the same network infrastructure.
- Multi-layer switches are often used in enterprise networks to optimize traffic flow, improve network performance, and support advanced features such as VLANs, QoS, and inter-VLAN routing.
Best Practices for Network Wiring:
1. Plan and Design:
- Conduct a thorough assessment of current and future networking requirements, including device placement, bandwidth needs, and growth projections.
- Create a detailed network topology diagram to visualize the layout of network components, including switches, routers, servers, and end-user devices.
2. Use Quality Cabling:
- Invest in high-quality Ethernet or fiber-optic cables that meet industry standards for performance and durability.
- Choose the appropriate cable type (e.g., Cat6, Cat6a, fiber) based on factors such as distance, bandwidth requirements, and environmental conditions.
3. Organize and Label:
- Implement structured cabling solutions to organize cables neatly and minimize clutter, reducing the risk of cable damage and signal interference.
- Label cables, patch panels, and network ports clearly to facilitate troubleshooting, maintenance, and future expansion.
4. Implement Redundancy:
- Deploy redundant network links and devices to ensure high availability and fault tolerance in case of link failures or equipment malfunctions.
- Use technologies such as link aggregation (e.g., EtherChannel) and spanning tree protocol (STP) to provide redundancy and load balancing across network paths.
5. Separate Data and Voice Traffic:
- Keep data and voice traffic on separate VLANs or physical networks to prevent interference and prioritize critical communication streams.
- Implement quality of service (QoS) policies to prioritize voice traffic and ensure low latency and high call quality for VoIP applications.
6. Secure Access Points:
- Secure network access points and distribution areas to prevent unauthorized access or tampering with network equipment.
- Use locking cabinets or enclosures to protect network switches, patch panels, and other infrastructure components from physical tampering or theft.
Conclusion:
By following best practices for network wiring and implementing multi-layer concepts suggested by CISCO, SMBs can build robust, scalable, and efficient network infrastructures that meet their current needs and future growth objectives. By investing in quality cabling, organizing and labeling network components, implementing redundancy and security measures, and leveraging multi-layer switches, organizations can ensure reliable connectivity, optimal performance, and seamless communication across their networks. Through careful planning, design, and implementation, SMBs can create a solid foundation for their digital infrastructure that supports their business operations and facilitates growth and innovation.
